NAMD, recipient of a 2002 Gordon Bell Award, a 2012 Sidney Fernbach Award, and a 2020 Gordon Bell Prize, is a parallel molecular dynamics code designed for high-performance simulation of large biomolecular systems. Based on Charm++ parallel objects, NAMD scales to hundreds of cores for typical simulations and beyond 500,000 cores for the largest simulations. NAMD uses the popular molecular graphics program VMD for simulation setup and trajectory analysis, but is also file-compatible with AMBER, CHARMM, and X-PLOR. NAMD is distributed free of charge with source code. You can build NAMD yourself or download binaries for a wide variety of platforms. Our tutorials show you how to use NAMD and VMD for biomolecular modeling.
Breaking News
|
NAMD 3.0.2 Release -
Point release 3.0.2 fixes bugs in the Colvars module that affect not only NAMD 3.0 and 3.0.1, but also earlier NAMD 2 versions. See announce.txt for details regarding correctness issues in: eigenvector, orientationAngle, orientation, both coordNum and selfCoordNum with pairlist, and distanceZ with dynamic axis. For more information about the bugs in Colvars, please see Colvars Bugfix Announcement. We encourage all NAMD users to upgrade to version 3.0.2. |
| NAMD 3.0 New Features - webpage is posted |
| NAMD GPU-resident benchmarks - results and data sets with GPU-optimized configuration posted |
| NAMD 2.15 ALPHA Release providing GPU-offload support for Intel GPU Max Series. This source code release available on the download page includes SYCL code that can be built using the Intel oneAPI toolkits. Following the download link reveals a page with detailed build instructions. |
Spotlight: Protein Hairpin and Parkinson's Disease (Jan 2016)
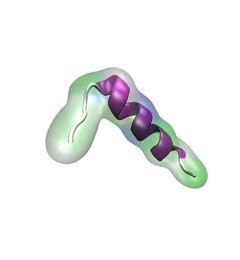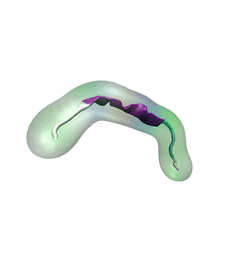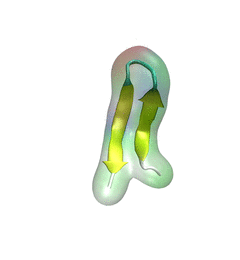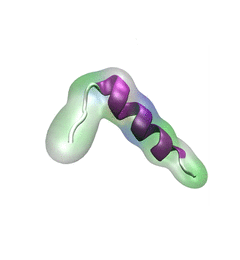
image size:
768.0KB
made with VMD
For centuries, millions of people around the globe have been troubled with a movement disorder that usually starts with a tremor in one hand. The disorder, later known as Parkinson's disease, affects commonly older individuals and disrupts patient's movement, sleep and speech from the brain. There is currently no cure for the disease. Key to the disease, progressively occurring in patient's brain, is the loss of neuron cells due to aggregation of a small protein named α-synuclein. Extensive studies have been carried out, yet the function of the protein remains a mystery. It is amazing that aggregation of such small proteins eventually leads to neuronal cell death and generates tremendous difficulties in peoples' life. In a recent report, a team of computational scientists attributed the cause of α-synuclein aggregation to a hairpin structure involving just a small region (amino acids 38-53) in the middle of the protein. With extensive simulations (over 180 μs in total), the researchers revealed that a short fragment encompassing region 38-53, exhibiting a high probability of forming a β-hairpin structure, is a key region during α-synuclein aggregation. Moreover, the researchers predicted a mutation that impedes β-hairpin formation, thereby retarding α-synuclein aggregation. The discoveries, made possible through the software NAMD and VMD, are expected to shed light on the mechanism underlying Parkinson's disease and to inspire the design of drugs. More on our α-synuclein website.
Overview
Why NAMD? (in pictures)
How to Cite NAMD
Features and Capabilities
Performance Benchmarks
Publications and
Citations
Credits and Development Team
Availability
Read the License
Download NAMD Binaries
(also VMD)
Build from Source Code
- Git access now available
Run at NCSA, SDSC, NICS, or Texas
Training
NAMD Developer Workshop in Urbana (August 19-20, 2019)
PRACE School on HPC for Life Sciences (June 10-13, 2019)
"Hands-On" Workshop in Pittsburgh (May 13-17, 2019)
Charm++ Workshop in Urbana (May 1-2, 2019)
Enhanced Sampling and Free-Energy Workshop (Sept 10-14, 2018)
NAMD Developer Workshop in Urbana (June 11-12, 2018)
"Hands-On" Workshop in Pittsburgh (May 21-25, 2018)
"Hands-On" QM/MM Simulation Workshop (April 5-7, 2018)
Older "Hands-On" Workshops
Support
Mailing List Issues for Yahoo.com Addresses
Announcements
NAMD 3.0.2 Release (Aug 2025)
NAMD 3.0.1 Release (Oct 2024)
NAMD 3.0 Release (Jun 2024)
NAMD 3.0 New Features (Feb 2024)
NAMD 2.14 Bug Fixes (Apr 2022)
NAMD 2.14 Release (Aug 2020)
NAMD 2.14 New Features
One-click NAMD/VMD in the cloud
QM/MM Interface to MOPAC and ORCA
QwikMD GUI Released in VMD 1.9.3
Previous Announcements
Documentation
Related Codes, Scripts, and Examples
NAMD Wiki (Recent Changes)
Older Documentation
News
Sparing healthy microbes while using a novel antibiotic

AMBER force field use in NAMD for large scale simulation

NAMD GPU-resident benchmarks available

NAMD and VMD share in COVID-19 Gordon Bell Special Prize
NAMD reference paper published online
Coronavirus Simulations by U. Delaware Team
Coronavirus Simulations on Frontera Supercomputer
Breakthrough Flu Simulations
Oak Ridge Exascale Readiness Program
Prepping for Next-Generation Cray at NERSC
Supercomputing HIV-1 Replication
How GPUs help in the fight against staph infections
Computational Microscope Gets Subatomic Resolution
Opening New Frontiers in the Battle Against HIV/AIDS
HIV Capsid Interacting with Environment
Assembling Life's Molecular Motor
Older News Items



