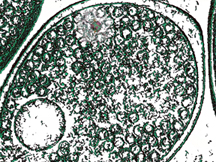
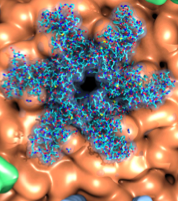
Cholesterol, an important fat molecule, regulates the structure and function of many membrane proteins. Computational studies of protein-cholesterol interactions have been long impeded by the slow dynamics of lipids like cholesterol. In a recent paper, Resource researchers report a new generation of an accelerated membrane model (HMMM) in which cholesterol can be included. Utilizing NAMD and in-house Tcl scripts with VMD, the new model successfully identifies cholesterol binding sites on proteins and captures detailed lipid interactions in agreement with experimental data.
The Future of Biomolecular Modeling
A 2015 TCBG Symposium brought together scientists from across the Midwest to brainstorm about what's on the horizon for computational modeling. See a summary of what these experts foresee.
Read more
A Look Ahead
The Urbana NIH Center previews what it will propose for the 2017-2022 funding cycle. By Lisa Pollack.
Read more
Announcements
Seminars
Remembering Klaus Schulten
Recent Publications All Publications
- Molecular dynamics simulations of biological membranes and membrane-associated phenomena across scales. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 2025.
- Cholesterol-targeting Wnt-β-catenin signaling inhibitors for colorectal cancer. Nat. Chem. Biol., 2025.
- Dissecting Large-Scale Structural Transitions in Membrane Transporters Using Advanced Simulation Technologies. J. Phys. Chem. B, 129:3703-3719. 2025.
- Modeling Diffusive Motion of Ferredoxin and Plastocyanin on the PSI Domain of Procholorococcus marinus MIT9313. J. Phys. Chem. B, 129:52-70. 2025.
- Membrane-bound model of the ternary complex between factor VIIa/tissue factor and factor X. Blood Adv., 9:729-740. 2024.
- Protein-Lipid Interactions in Priming the Bacterial Translocon. Membranes, 14:249. 2024.
- Atomistic characterization of β2-glycoprotein I domain V interaction with anionic membranes. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 22:3277-3289. 2024.
Highly Cited
NAMD2: Greater scalability for parallel molecular dynamics. Journal of Computational Physics, 151:283-312, 1999.
Click here for other highly cited papers
Click here for other highly cited papers