Highlights of our Work
2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 | 2002 | 2001
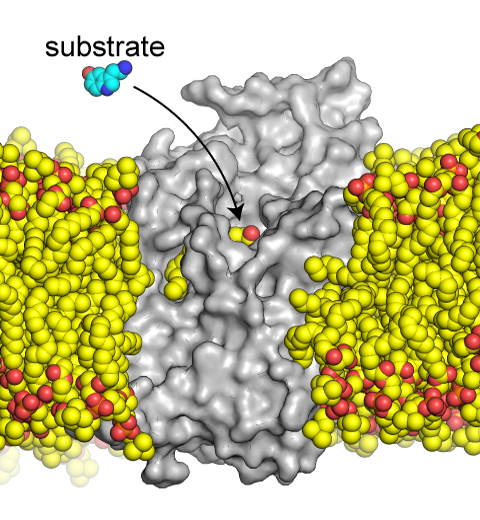
The serotonin transporter (SERT) is a protein in the cellular membrane of neurons that is responsible for the uptake of the neurotransmitter serotonin from the synapse back into the cell. Lipid-protein interactions have been demonstrated to regulate the transport properties of SERT. To understand the underlying mechanism, we collaborated with Eric Gouaux's lab at OHSU and investigated the binding of lipids to SERT using cryo-EM and molecular dynamics simulations. Our enhanced sampling simulations (performed in NAMD and analyzed in VMD) successfully captured a specific lipid that binds to a binding site in SERT. This site can also accommodate the substrate serotonin to trigger its transport. Therefore, binding of lipids to it is a putative mechanism for lipid-modulated function of SERT. For more details, see our recent publication in PNAS.