Highlights of our Work
2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 | 2002 | 2001
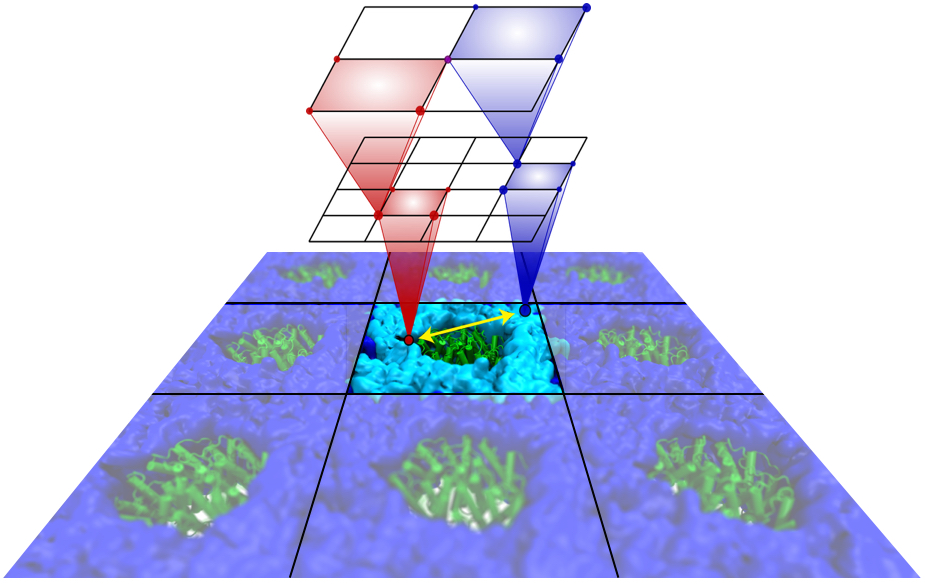
Long-range electrostatic interactions control macromolecular processes
within living cells as prominent charges appear everywhere,
such as in DNA or RNA,
in membrane lipid head groups, and in ion channels. Reliable and
efficient description of electrostatic interactions is crucial in
molecular dynamics simulations of such processes. Recently a new
mathematical approach for calculating electrostatic interactions, known as
multilevel summation method (MSM),
has been developed and
programmed into
NAMD 2.10
as reported
here.
Compared to the earlier decades-long approach,
the particle-mesh Ewald (PME) method, MSM provides more flexibility
as it permits non-periodic simulations like ones
with asymmetric charge distributions
across a membrane
or of a water droplet with a protein folding inside. Furthermore,
MSM is ideally suited for modern parallel computers, running,
for example, simulations
of large virus particles. More information
here.