Highlights of our Work
2026 | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 | 2002 | 2001
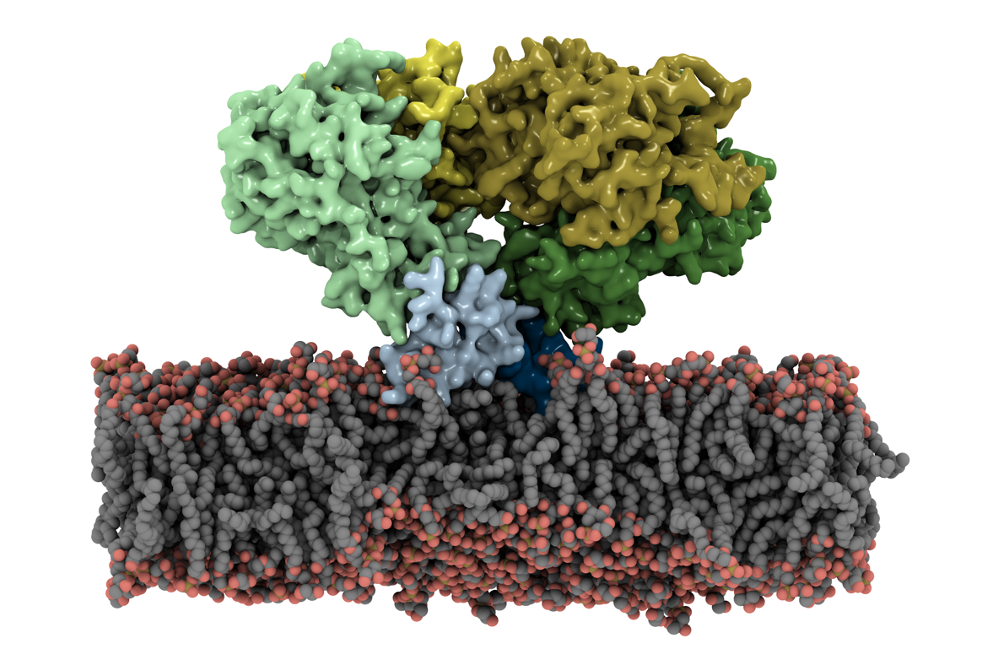
Staphylococcus aureus, a prominent human pathogen, employs a specific enzyme to evade the immune system. This enzyme converts antimicrobial fatty acids in the cellular membrane into anti-inflammatory compounds that protect the pathogen against the host inflammatory response. Understanding the membrane-binding mechanism of this enzyme is essential for developing new strategies to combat S. aureus infections.
As highlighted in our recent publication in J. Biol. Chem., Resource researchers employed molecular dynamics simulations using NAMD to study this mechanism. Utilizing a specifically designed membrane model with enhanced lipid motion, they captured how the enzyme binds to the membrane and described its pose within the membrane. These findings provide molecular insights into S. aureus' virulence and highlight potential targets for novel therapeutic interventions.