Highlights of our Work
2025 | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 | 2002 | 2001
2.7 release
of NAMD
includes GPU acceleration,
downloadable binaries
for Linux clusters with InfiniBand networks,
grid-based forces and ..." />
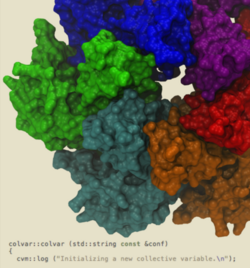

image size:
994.9KB
made with VMD
The eagerly awaited 2.7 release
of NAMD
includes GPU acceleration,
downloadable binaries
for Linux clusters with InfiniBand networks,
grid-based forces and extra bond/angle/torsion conformational restraints
for molecular dynamics flexible fitting (MDFF), and a major
enhancement of both alchemical and conformational free energy methods.
Alchemical calculations gradually alter the chemical structure of a
molecule during a simulation, monitoring the consequences of creating and
deleting atoms via either free energy perturbation or thermodynamic
integration.
A soft-core correction may be employed to
circumvent singularities when atoms are created.
Conformational calculations can probe structural rearrangements along
an arbitrary number of collective variables,
including distances between atoms or groups of atoms, distances projected
along an axis or in a plane, angles, torsions, eigenvectors,
gyration radii, coordination, root mean-square displacements, orientations,
and alpha-helicity. New variables can be introduced without recompilation.
Free energy surfaces or potentials of mean force can be constructed using
metadynamics, the adaptive biasing force method, umbrella sampling, and
steered molecular dynamics.
The collective variables capability of NAMD
has allowed the simulation of the
illustrated hexameric helicase. In the simulation, a single strand of DNA
passes through the central core while the hexamer translocates or "walks"
along the DNA, a mechanical process driven by the energy of ATP hydrolysis.



