Case Studies
The case studies provided on this page exploit the molecular graphics program VMD for teaching molecular cell biology. The case studies start out like a conventional textbook chapter, but utilize VMD molecular graphics to offer a much more detailed view of the subjects than commonly possible in textbooks. The case studies induce the reader to inspect by means of VMD the systems introduced. For this purpose the case studies show the molecular systems through graphical images, but provide also the files that permit the reader to regenerate the images with few mouse clicks and then explore in depth the structures shown using the program VMD. Students can rotate the images, enlarge them, alter the views in many ways, and analyze structures and sequences. The readers, undergraduate or graduate students, are expected to have a basic familiarity with the molecular graphics program VMD that is achieved best by completing the "Using VMD" tutorial.
The case studies below introduce various, simple, yet relevant and interesting subjects also found in textbooks. Readers will be amazed how much more they learn reading the case studies not in a passive manner, but in an active manner by using VMD.

- Viruses are the smallest life form in existence. Satellite Tobacco Mosaic Virus (STMV) is one of the simplest viruses. STMV has a protective outer coat consisting of 60 identical proteins. The coat surrounds the virus's genetic material, in this case a ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecule. STMV will be explored in this case study to illustrate the principles of virus structure . . .
- STMV Case Study [pdf, 6.2M]
- Required case study files: [.tgz, 29.4M]

- Water is essential for sustaining life on Earth. Almost 75% of the Earth's surface is covered by it. It composes roughly 70% of the human body by mass. It is the medium associated with nearly all microscopic life processes. Much of the reason that water can sustain life is due to its unique properties...
- Water Case Study [pdf, 1.1M]
- Required case study files: [.tgz, 65.3M]
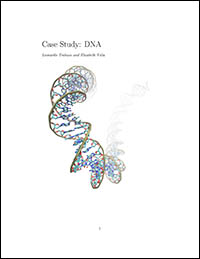
- With the 50th aniversary of the discovery of the DNA structure by James Watson and Francis Crick and the race for the human genome, with all its controversies and awe-inspiring medical implications, we have all heard a lot about DNA, the molecule of life...
- DNA Case Study [pdf, 2.0M]
- Required case study files: [.tgz, 81.3M]

- Membranes are essential to cellular organisms. They are like fortresses in that they provide a barrier between the inside and outside with guarded drawbridges in the form of proteins that regulate the influx and efflux of material. Unlike the rigid walls of a fortress, membranes are fluid and are able to bend and move. The bricks forming a membrane, called lipids, freely move. Plasma membranes enclose and define the boundaries of a cell, maintaining a barrier between the interior of a cell, the cytosol, and the extracellular environment...
- Bilayer Case Study [pdf, 1003k]
- Required case study files: [.tgz, 39.2M]

- Bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI) is one of the smallest and simplest globular proteins that inhibits protein digestive action (digesting protein to peptides) of the enzyme trypsin in cow (bovine) pancreas. BPTI is a member of the family of serine protease inhibitors. These enzymes have many conserved cysteines that form disulfide bonds that stabilize protein three-dimensional structures. BPTI has a relatively broad specificity in that it can inhibit several kinds of digestive enzymes...
- BPTI Case Study [pdf, 4.9M]
- Required case study files: [.tgz, 27.6M]

- Without a doubt, the most organized and coordinated machine known is the biological cell. Inside its micrometer-scale diameter, a wide variety of macromolecules (DNA, proteins, sugars, lipids, etc.) work together in a cooperative way, balancing energy and matter to keep the cell alive. To maintain harmony and efficiency between various functions, most processes have to be turned on or off according to different cellular stages and changes within the environment. To this end, together with the mechanisms to assemble functional proteins and to turn on their functions, there should be counterparts to suppress and disassemble proteins when they are no longer needed. Ubiquitin is a key player in eukaryotic intracellular protein degradation...
- Ubiquitin Case Study [pdf, 1.7M] Required case study files: [.tgz, 40.2M])

- Myoglobin is a small, monomeric protein which serves as an intracellular oxygen storage site. It is found in abundance in the skeletal muscle of vertebrates, and is responsible for the characteristic red color of muscle tissue. Myoglobin is closely related to hemoglobin, which consists of four myoglobin-like subunits that form a tetramer and are responsible for carrying oxygen in blood. In humans, blood-borne cardiac myoglobin can serve as a biomarker of heart attack, since blood myoglobin levels rise in two to three hours following muscle injury...
- Myoglobin Case Study [pdf, 2.8M]
- Required case study files: [.tgz, 63.5M])

- The organization of water is critical to most biological processes. Although cell membranes are to some extent water-permeable, they cannot facilitate the rapid exchange of large volumes of water, as required by the kidneys in the human body. Aquaporins (AQPs) are a family of specialized integral membrane proteins which function mainly as water channels. These highly efficient water channels can explain how we secrete tears, saliva and sweat, how our kidneys concentrate urine, and how our brains maintain spinal fluids...
- Aquaporin Case Study [pdf, 3.2M]
- Required case study files: [.tgz, 16.9M]
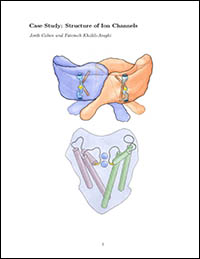
- The physiological function of ion channels had been observed long before they were known to exist. Many cells such as nerve and muscle cells, were known to have excitable cell membranes that would respond to variations in their electrical membrane potential through an all-or-nothing response. It was soon discovered that the regulators of ion passage across biological membranes were specialized proteins called ion channels. Ion channels are transmembrane proteins that selectively allow a given species of ions to pass through them...
- Ion Channels Case Study [pdf, 3.0M]
- Required case study files: [.tgz, 13.4M]

- In the extreme sport of bungee jumping, a daring athlete leaps from a great height and free-falls while a tethered cord tightens and stretches to absorb the energy from the descent. The bungee cord protects the jumper from serious injury, because its elasticity allows it to extend and provide a cushioning force that opposes gravity during the fall. Amazingly, nature also uses elasticity to dampen biological forces at the molecular level, such as during extension of a muscle fiber under stress. The molecular bungee cord that serves this purpose in the human muscle fiber is the protein titin, which functions to protect muscle fibers from damage due to overstretching...
- Titin Case Study [pdf, 992k]
- Required case study files: [.tgz, 52.6M])
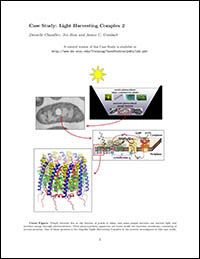
- Sunlight is ultimately the energy source for nearly all life on Earth. Many organisms, such as plants, algae, and some bacteria, have developed a means to harvest sunlight and turn it into chemical energy, a process known as photosynthesis. Photosynthesis occurs with an amazingly high efficiency, not surprising given the more than 3.5 billion years of evolution...
- LH2 Case Study [pdf, 13.0M]
- Required case study files: [.tgz, 1.7M])
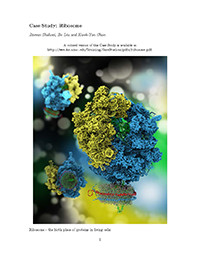
- The ribosome, one of the largest molecular machines in living cells, is in charge of protein synthesis. The ribosome translates genetic code into amino acid sequences that fold into protein structures. Ribosomes are the birth place of proteins in living cells. The bacterial ribosome plays also a key role in medicine as a drug target for antibiotics. Antibiotics are employed by biological cells, for example those arising in molds, to fight bacteria...
- Ribosome Case Study [pdf, 10.0M]
- Required case study files: [.tgz, 48.0M])



