

Next: Required software
Up: Rosetta/MDFF Tutorial
Previous: Contents
Contents
Hybrid structure analysis strategies, which combine structural data from
sources such as X-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) with
computational modeling, have become successful means for resolving
structural models of macromolecular complexes found in living cells. The computational
modeling tools employed in these strategies usually aim to automate the whole process
of structure analysis in order to avoid human bias, yet the experience of
structural biologists may actually be a desirable factor in structure
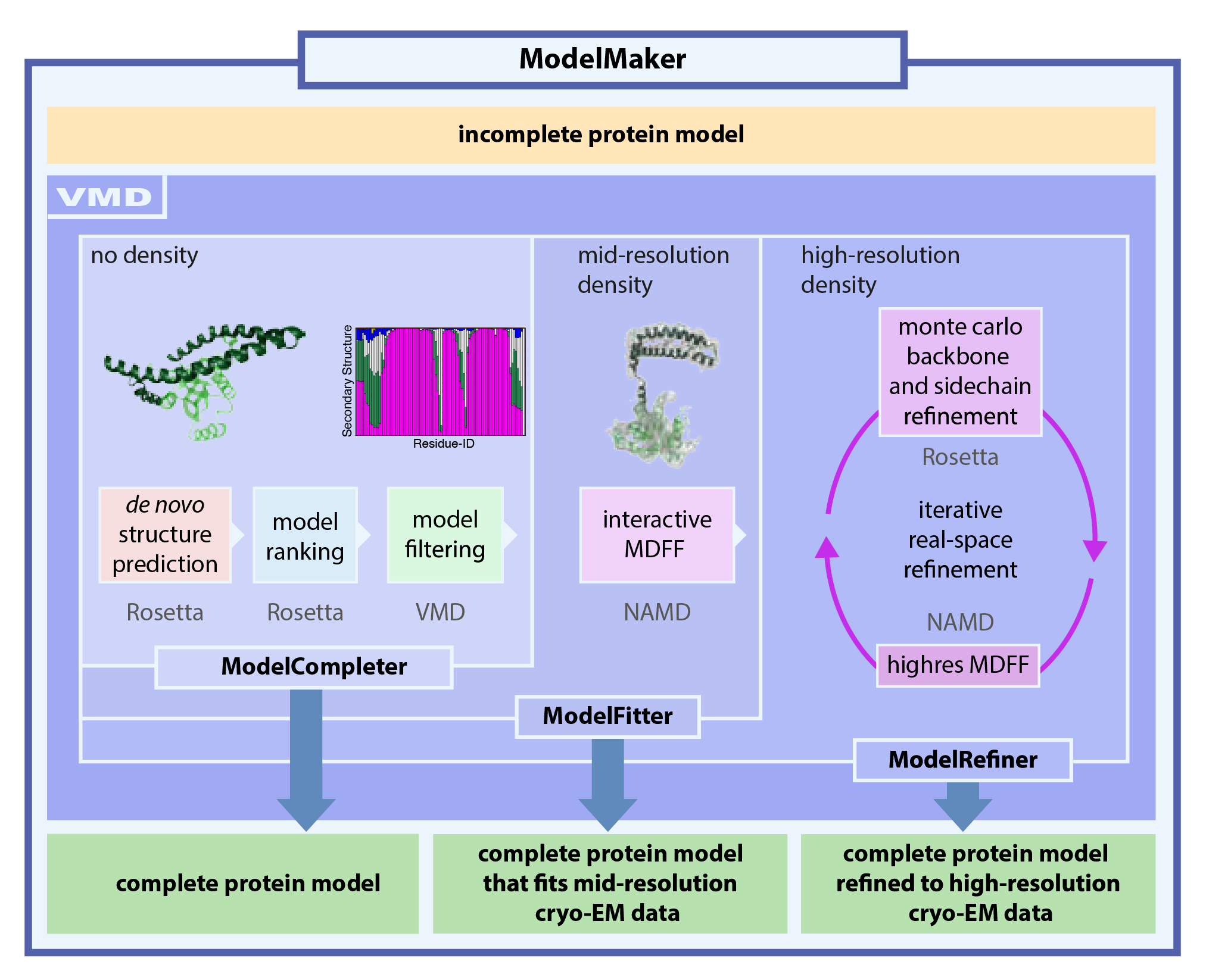
refinement. Here, we present a tool, named ModelMaker, to interactively build
complete models guided by incomplete structural data from experiments,
automated structure prediction, and user expertise. With ModelMaker, incomplete
models are completed by generating ensembles of models of the
missing segments with de novo structure prediction in Rosetta. Then, a
single complete model is obtained by ensemble filtering through
sorting, clustering, and secondary structure analysis. This model is further refined
in real space to fit mid- or high-resolution cryo-EM densities through a combination of
molecular dynamics flexible fitting (MDFF) with monte carlo based backbone and sidechain
rotamer search algorithms in an iterative manner. ModelMaker is found to be of particular value for modeling
the missing highly flexible or multi-conformational domains of large macromolecular
complexes with sparse density as well as refining models to high-resolution densities.
Furthermore, ModelMaker can be employed to complete missing segments of structures without
any density information to obtain complete structures to initiate molecular dynamics simulations.
ModelMaker is a tool that takes advantage of the popular and user-friedly molecular visualizaion
software VMD that provides an easy-to-use environment to run the usually very complex computational
modeling tools.
In this tutorial the application of ModelMaker is demonstrated by completing the C-terminus (3) and a structurally
unresolved protein insertion (4) of the
X-ray structure of the proteasomal subunit Rpn11 in yeast (chain B of PDB ID 4OCM)
and fit it to the mid-resolution (7.7 Å) cryo-EM density of Rpn11
derived from the cryo-EM density of the yeast 26S proteasome (EMD-2594) (5).
The quality of the model generated by ModelMaker is proven by comparison to the structure of
Rpn11 (chain G of PDB-ID 3JCK) derived from a high-resolution
cryo-EM density (3.5 Å). The generated model of yeast
Rpn11 serves as basis for a homology model of human Rpn11 (6)
which is then further refined through ModelMaker to fit the high-resolution cryo-EM
density (3.9 Å) of the human 26S proteasome (EMD-4002) (7).
In a similar manner as shown in this tutorial for the Rpn11 example, ModelMaker
was employed to derive the structure of the human 26S proteasome (PDB ID 5L4G and 5L4K) from a 3.9 Åcryo-EM density of the human 26S proteasome (EMD-4002).
We recommend completing the QwikMD/MDFF, VMD, and MDFF tutorial first.
QwikMD/MDFF: http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/~trudack/QwikMDFF/
VMD: http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Training/Tutorials/vmd/tutorial-html/
MDFF: http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Training/Tutorials/science/mdff/tutorial_mdff-html/



Next: Required software
Up: Rosetta/MDFF Tutorial
Previous: Contents
Contents
www.ks.uiuc.edu/Training/Tutorials