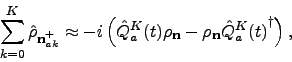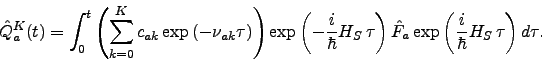


Next: Integrating the HEOM
Up: Introduction and theory
Previous: Correlation functions
Contents
The exponential terms in Eq. 14 lead to a hierarchy of matrices 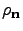 (t), called auxiliary density matrices (ADMs), to take into account the non-Markovian evolution of
(t), called auxiliary density matrices (ADMs), to take into account the non-Markovian evolution of 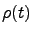 . The ADMs are indexed by a vector
. The ADMs are indexed by a vector
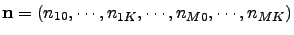 and coupled through the index operators
and coupled through the index operators
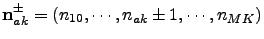 . The hierarchy equations of motion are
. The hierarchy equations of motion are
More simply written as
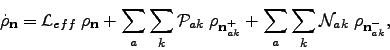 |
(21) |
where
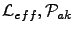 and
and
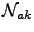 are Liouville space operators
are Liouville space operators 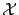 , such that
, such that
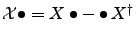 for the corresponding Hilbert space operator
for the corresponding Hilbert space operator 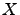 . Any ADM with a negative in the index vector
. Any ADM with a negative in the index vector 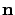 is set to 0.
is set to 0.
The ADMs need to be truncated to a finite number. Each ADM can be assign to a level
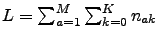 . There are two ways to truncate the hierarchy of ADMs to some level
. There are two ways to truncate the hierarchy of ADMs to some level 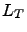 : time non-local (TNL) truncation and time local (TL) truncation. In case of TNL truncation, all ADMs with
: time non-local (TNL) truncation and time local (TL) truncation. In case of TNL truncation, all ADMs with 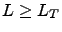 is set to zero. In case of TL truncation, all ADMs with
is set to zero. In case of TL truncation, all ADMs with 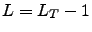 the Markovian approximation is assumed, such that
the Markovian approximation is assumed, such that
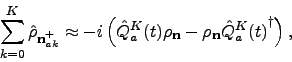 |
(22) |
where
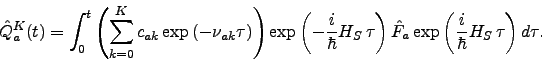 |
(23) |



Next: Integrating the HEOM
Up: Introduction and theory
Previous: Correlation functions
Contents
http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Research/phi
![$\displaystyle -\frac i \hbar \left[ H_S, \rho_{\bf n}\right]-\sum_{a=1}^M\sum_{k=0}^K n_{ak}\nu_{ak} \rho_{\bf n}$](img71.gif)
![$\displaystyle -\sum_{a=1}^M\left(\frac{2\lambda_a}{\beta\hbar^2\gamma_a}-\sum_{...
...{c_{ak}}{\hbar\nu_{ak}}\right)\left[ F_a,\left[ F_a, \rho_{\bf n}\right]\right]$](img72.gif)
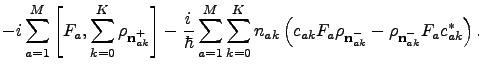
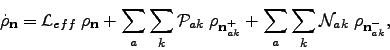
![]() . There are two ways to truncate the hierarchy of ADMs to some level
. There are two ways to truncate the hierarchy of ADMs to some level ![]() : time non-local (TNL) truncation and time local (TL) truncation. In case of TNL truncation, all ADMs with
: time non-local (TNL) truncation and time local (TL) truncation. In case of TNL truncation, all ADMs with ![]() is set to zero. In case of TL truncation, all ADMs with
is set to zero. In case of TL truncation, all ADMs with ![]() the Markovian approximation is assumed, such that
the Markovian approximation is assumed, such that